16. Source code¶
Contents
Source code on Github¶
Warning
The source code is free, but we can give only limited support, due to limited person power!
Source code¶
-------------------------------------------------- ######## ## ## #### ###### ## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #### #### ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #### ## ## ## ## ## ######## ## ## ## ## ## ## #### ## ## ## ## ## ## ## #### #### ## ## ## ## ## ########## ## ## ## ## ## ## ## Community WATer Model --------------------------------------------------
Modules of CWatM¶
The source code of CWatM has a modular structure. Modules for data handling, output, reading as parsing the setting files are in the management_modules folder.
![digraph {
compound=true
overlap=false
graph [layout = neato]
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=red,fixedsize=true,width=1.3,fontsize=23] cwatm_model;
node [shape=box,style = filled,fillcolor=Tomato,fontsize=14,width=3] dynamicModel;
node [shape=box,style=filled,fillcolor=orange,fontsize=14,width=2] data_handling; configuration; globals; messages; output; replace_pcr; timestep; checks;
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=Tomato,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] cwatm_initial;cwatm_dynamic;
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=Azure,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] miscInitial; initcondition; landcoverType;
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=lightblue,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] readmeteo; inflow; interception; evaporationPot; evaporation; snow_frost; sealed_water;
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=DodgerBlue,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] soil; evaporation;capillarRise;groundwater;
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=MediumOrchid,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] waterbalance; environflow
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=MediumOrchid,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] water_demand; environmental_need, domestic, industry, irrigation, livestock
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=RoyalBlue,fixedsize=true,width=1.0] routing_kinematic; runoff_concentration; lakes_reservoirs; lakes_res_small
node [shape=circle,style=filled,fillcolor=RoyalBlue,fixedsize=true,width=0.8] routing_sub; "t5.dll"
cwatm_model -> dynamicModel[color=red,penwidth=3.5];
dynamicModel -> cwatm_initial[color=Tomato,penwidth=2.5];
dynamicModel -> cwatm_dynamic[color=Tomato,penwidth=2.5];
cwatm_model -> globals
cwatm_model -> configuration
cwatm_initial -> miscInitial[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> initcondition[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> landcoverType[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> inflow[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> readmeteo[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> evaporationPot[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> snow_frost[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> runoff_concentration[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> lakes_reservoirs[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> lakes_res_small[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> soil[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> evaporation[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> environflow[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> groundwater[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> water_demand[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_initial -> routing_kinematic[color=RoyalBlue3];
cwatm_dynamic -> landcoverType[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> inflow[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> readmeteo[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> evaporationPot[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> snow_frost[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> sealed_water[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> runoff_concentration[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> lakes_reservoirs[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> lakes_res_small[color=MidnightBlue];
landcoverType -> soil[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> environflow[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> evaporation[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> capillarRise[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> groundwater[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> interception[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> water_demand[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> routing_kinematic[color=MidnightBlue];
cwatm_dynamic -> waterbalance[color=MidnightBlue];
water_demand -> domestic[color=MidnightBlue];
water_demand -> industry[color=MidnightBlue];
water_demand -> livestock[color=MidnightBlue];
water_demand -> irrigation[color=MidnightBlue];
water_demand -> environmental_need[color=MidnightBlue];
routing_kinematic -> lakes_reservoirs[color=MidnightBlue];
routing_kinematic -> routing_sub[color=MidnightBlue];
routing_kinematic -> "t5.dll"[color=MidnightBlue];
routing_sub -> "t5.dll"[color=MidnightBlue]
cwatm_initial -> data_handling[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0];
readmeteo -> data_handling[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
cwatm_dynamic -> output[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0];
cwatm_dynamic -> timestep[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0];
data_handling -> checks[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
data_handling -> messages[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
data_handling -> timestep[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
output -> messages[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
output -> timestep[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
readmeteo -> checks[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
water_demand -> replace_pcr[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
waterbalance -> replace_pcr[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
routing_kinematic -> replace_pcr[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
lakes_reservoirs -> replace_pcr[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
lakes_res_small -> replace_pcr[penwidth=0.5, style=dashed, arrowsize =0]
}](_images/graphviz-7e68b445b6cf242c4f14d98a3008ec8e67606ddf.png)
Figure 1: Schematic graph of CWatM modules
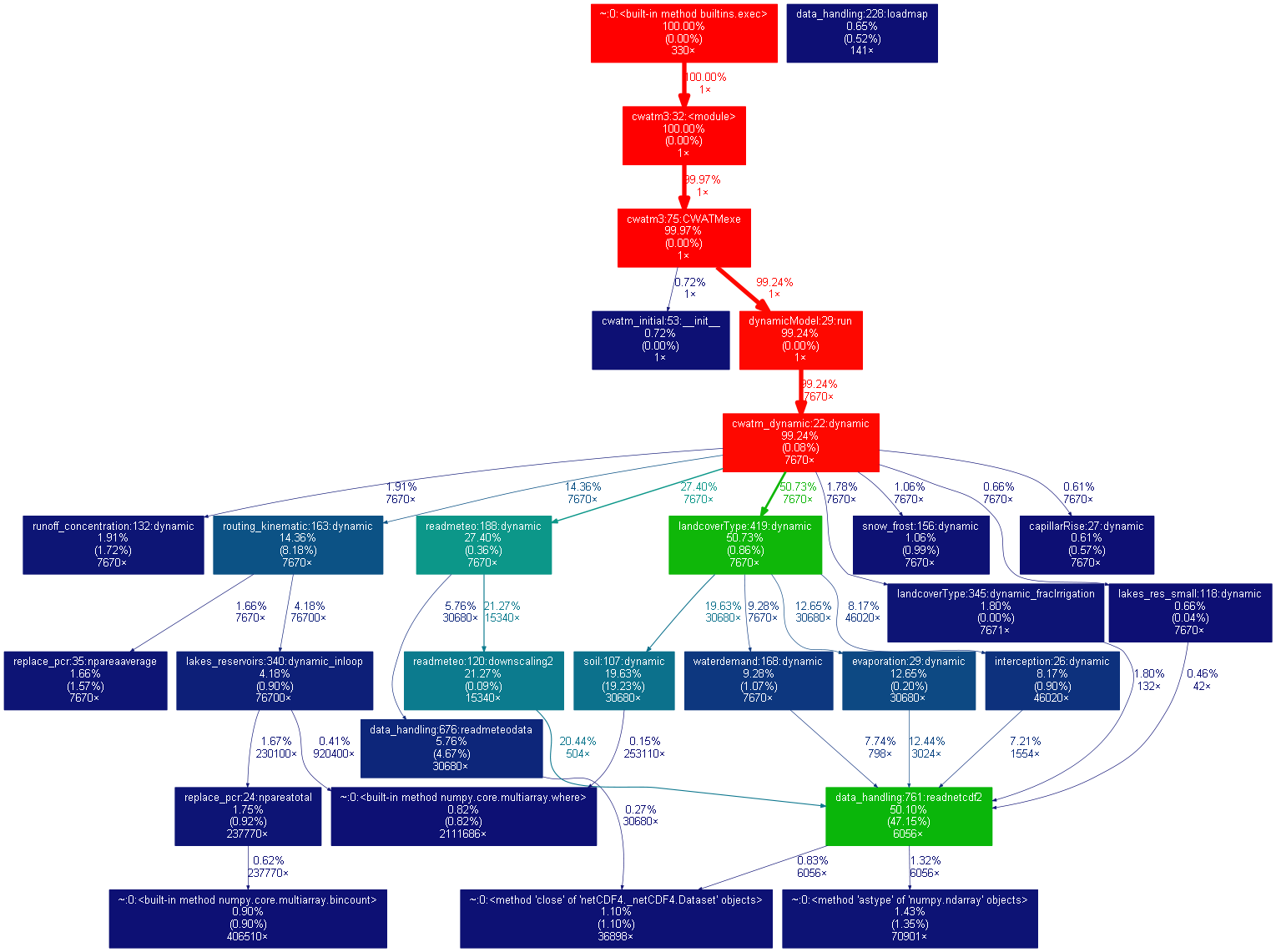
Figure 2: Graphical profile of CWatM run for Rhine catchment from 1/1/190-31/12/2010
Note
Source code description¶
- run_cwatm
- cwatm_model module
- cwatm_dynamic module
- cwatm_initial module
- hydrological_modules package
- management_modules package
Download Manual as pdf¶
Burek, P., Smilovic, M., Guillaumot, L., de Bruijn, J., Greve, P., Satoh, Y., Islaam, A., Virgen-Urcelay, A., Tang, T., Kahil, T., and Wada, Y.: Community Water Model CWatM Manual, Laxenburg, Austria, IIASA Report, 2020.
Global dataset¶
Remarks¶
We as developers belief that CWatM should be utilize to encourage ideas and to advance hydrological, environmental science and stimulate integration into other science disciplines.
CWatM is based on existing knowledge of hydrology realized with Python and C++. Especially ideas from HBV, PCR-GLOBE, LISFLOOD, H08, MatSiro, WaterGAP are used for inspiration.
Your support is more then welcome and highly appreciated Have fun!
The developers of CWAT Model