2. Model Design¶
Contents
Background¶
Water Futures and Solutions Initiatives (WFAS)¶
Water Futures and Solutions Initiatives is using a multi-model approach for global climatic, hydro-socioeconomic modeling in order to assess possible futures. We use three leading global hydrological models H08, WaterGAP and PCR-GLOBWB for estimating water demand and supply. This approach is used for a better understanding of the uncertainty and limitations of modeling. It provides a degree of confidence in the results an is in-line with the ISI-MIPS approach of multi-modeling
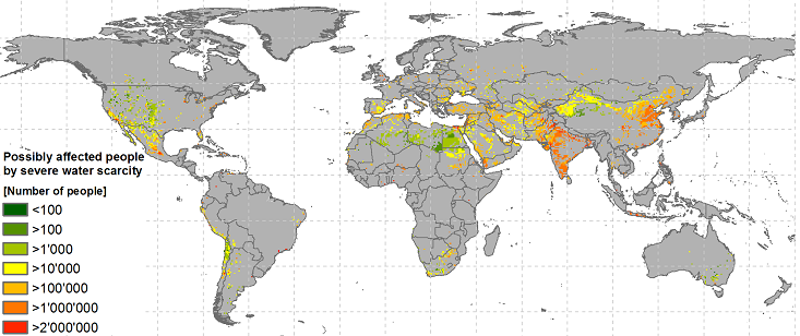
Figure 1: Potential population under severe water scarcity in 2050 - Middle of the Road Scenario - WFAS fast-track analysis
Nexus Integration - Water Energy Food Environment¶
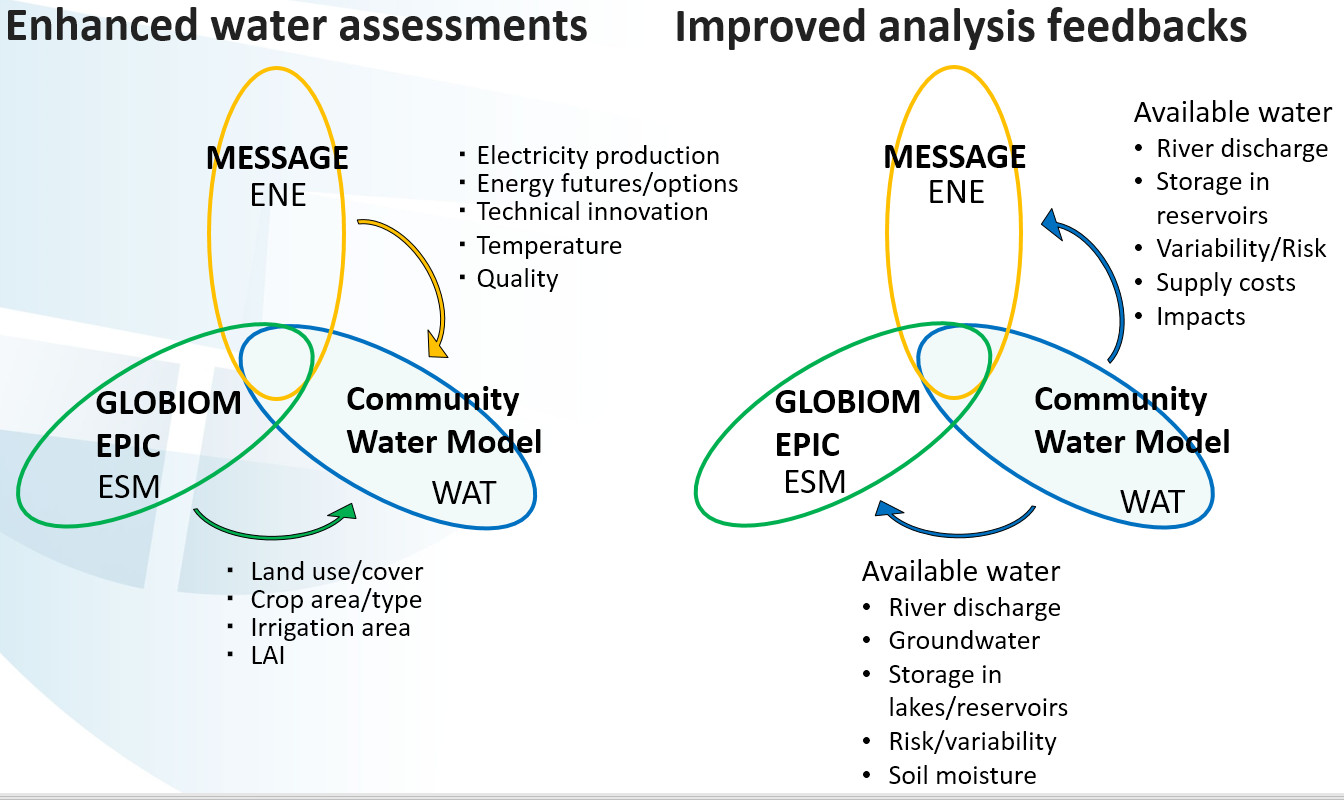
Figure 2: IIASA model interactions
CWAT and the IIASA global hydro-economic model¶
The Community Water Model will help to develop a next-generation hydro-economic modeling tool that represents the economic trade-offs among water supply technologies and demands. The tool will track water use from all sectors and will identify the least-cost solutions for meeting future water demands under policy constraints. In addition, the tool will track the energy requirements associated with the water supply system (e.g., desalination and water conveyance) to facilitate the linkage with the energy-economic tool. The tool will also incorporate environmental flow requirements to ensure sufficient water for environmental needs. The new hydro-economic model will be linked to CWatM by GAMS output and input files (gdx-files).
Model design and processes¶
Design¶
The Community Water Model (CWatM) will be designed for the purpose to assess water availability, water demand and environmental needs. It includes an accounting of how future water demands will evolve in response to socioeconomic change and how water availability will change in response to climate.
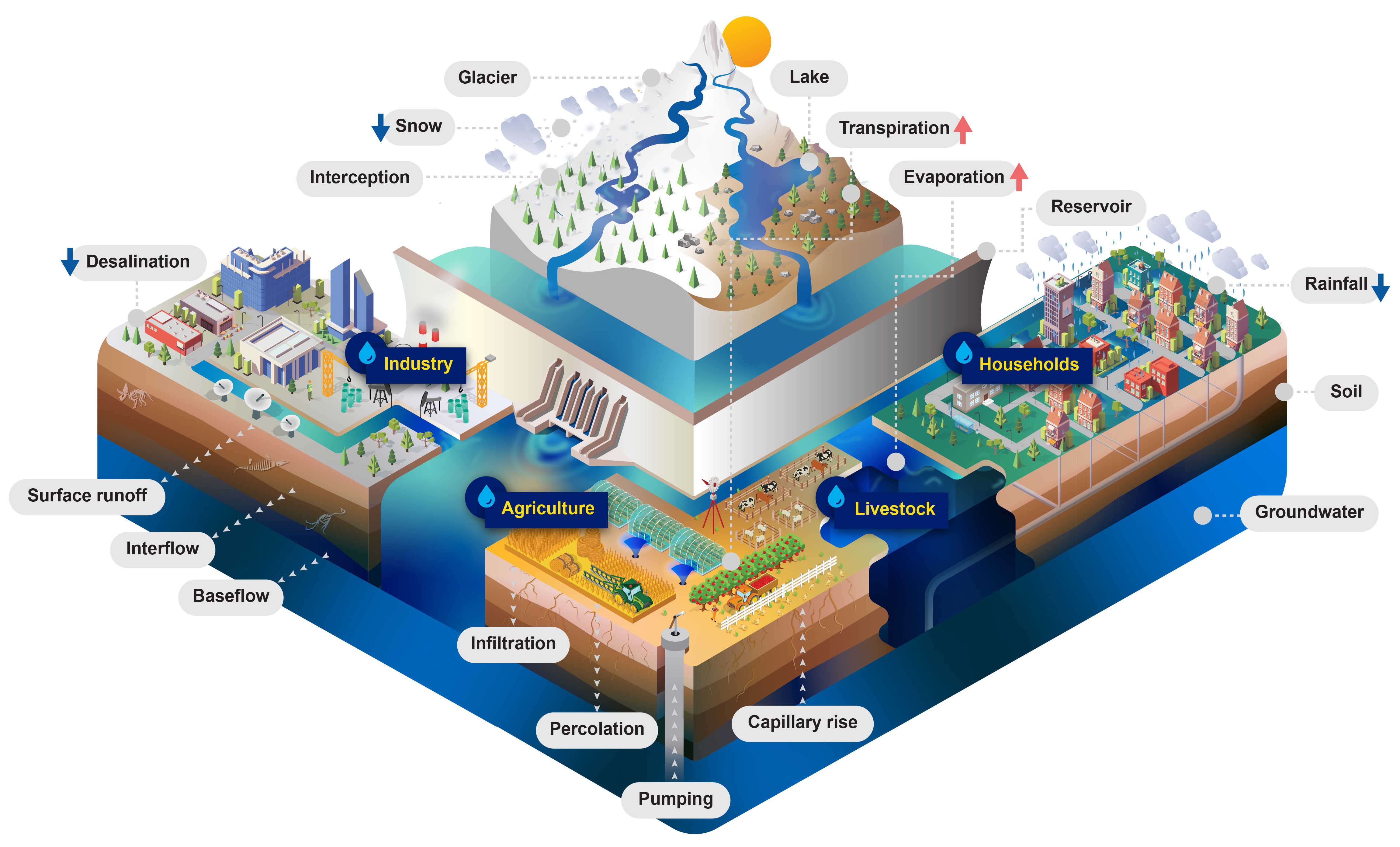
Figure 3: CWatM - Water related processes included in the model design
Processes¶
Calculation of potential Evaporation¶
Using Penman-Montheith equations based on FAO 56
Calculation of rain, snow, snowmelt¶
Using day-degree approach with up to 10 vertical layers Including snow- and glacier melt.
Land cover¶
using fraction of 6 different land cover types
Forest
Grassland
Irrigated land
Paddy irrigated land
Sealed areas (urban)
Water
Water demand¶
including water demand from industry and domestic land use via precalculated monhly spatial maps
including agricultural water use from calculation of plant water demand and livestock water demand
Return flows ((water withdrawn but not consumed and returned to the water circle)
Vegetation¶
Vegetation taken into account for calculating
Albedo
Transpiration (including rooting depth, crop phenology, and potential evapotranspiration)
Interception
Soil¶
Three soil layers for each land cover type including processes:
Frost interupting soil processes
Infiltration
Preferential flow
Capillary rise
Surface runoff
Interflow
Percolation into groundwater
Groundwater¶
Groundwater storage is simulated as linear groundwater reservoir
Lakes & Reservoirs¶
Lakes are simulated with weir function from Poleni for rectangular weir.
Reservoirs are simulated as outflow function between three storage limits (conservative, normal,flood) and three outflow functions (minimum, normal, non-damaging)
Routing¶
Routing is calculated using the kinematic wave approach
Features of the Model¶
Community Model¶
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Programming Language |
Python 3.x with some C++ for computational demanding processes e.g. river routing |
Community driven |
Open-source but lead by IIASA GitHub repository |
Well documented |
Documentation, automatic source code documentation GitHub Docu |
Easy handling |
Use of a setting file with all necessary information for the user Complete settings file and Output Meta NetCDF information |
Multi-platform |
Python 3.x on Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix - to be used on different platforms (PC, clusters, super-computers) |
Modular |
Processes in subprograms, easy to adapt to the requirements of options/ solutions Modular structure |
Water Model¶
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Flexible |
different resolution, different processes for different needs, links to other models, across sectors and across scales |
Adjustable |
to be tailored to the needs at IIASA i.e. collaboration with other programs/models, including solutions and option as part of the model |
Multi-disciplinary |
including economics, environmental needs, social science perspectives |
Sensitive |
Sensitive to option / solution |
Fast |
Global to regional modeling – a mixture between conceptional and physical modeling – as complex as necessary but not more |
Comparable |
Part of the ISI-MIP community |